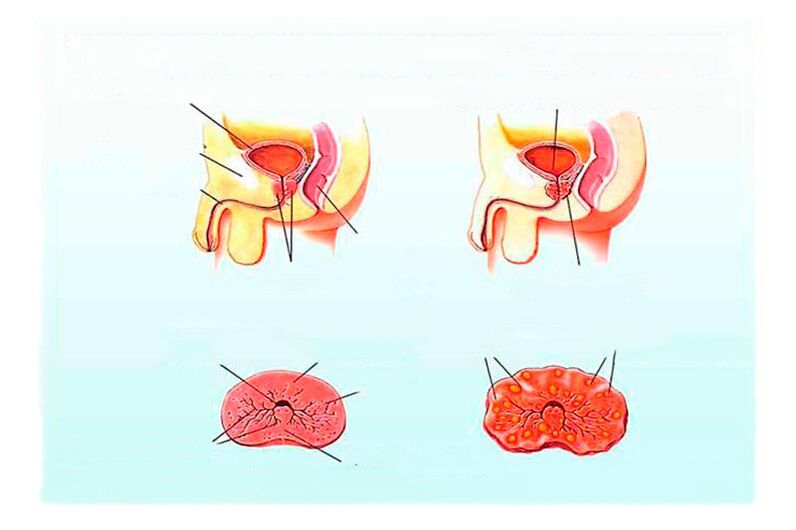
Chronic prostatitis is a prolonged inflammation that occurs due to infection or concomitant pathologies in the prostate gland.
Chronic prostatitis is diagnosed in men of all ages.According to statistics, this disease is the most common reason for a visit to a urologist in patients under 50.Chronic, a bacteriological examination reveals the pathogen only in 5-10% of patients.In most cases, other factors are considered the cause of the disease.It is known that the presence of an infection is not a prerequisite for the appearance of the disease.The chronic inflammation of the prostate is a polethiological pathology, which is the result of the actions of various causes and provocative factors.In 90-95% of patients, antibacterial therapy has limited effectiveness or is not required at all.
Classification of chronic prostatitis
The classification of chronic prostatitis by etiological characteristic distinguishes between two main forms of the disease: chronic (infectious) bacterial prostatitis and chronic non -bacterial (aseptic) prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain (KTS).
The etiological classification of chronic prostatitis includes:
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- Chronic non -bacterial (aseptic)/CTB ("prostatini" or "painful prostatic gland" is an obsolete term used to determine pathology).
- Non -bacterial (aseptic) CTB prostatitis with an inflammatory component (leukocyte concentration increases significantly in the secret of the prostate, sperm, the first part of the urine).
- Chronic non -bacterial (aseptic)/CTB prostatitis without an inflammatory component (concentration of white blood cells in the secret of prostate, sperm, the first part of the urine is insufficient for inflammation).
- Ashmptomic chronic prostatitis (detected in laboratory studies is not clinically shown).
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a rare pathology, as can be seen in previous statistics.The infection is the cause of the chronic recurring inflammation of the prostate in one of the ten patients.Pathology is often associated with other infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs.Most of the time, its cause is a non -specific infection, however, in the presence of STSPP, chronic inflammation of the gland can be caused by chlamydia, ureplasmosis, mycoplasmosis or other specific microorganisms.
Chronic non -bacterial (aseptic) prostatitis, or chronic pain syndrome, is a long -term recurrent disease that occurs as a result of the aseptic inflammation of the prostate.This is a little study pathology.In the presence of symptoms of the disease, the tests determine the white blood cells in the secret of the gland, in the seed fluid, in the initial portion of the urine, but the results of the bacteriological examination are negative.In other cases, there are no signs of infection, nor leukocytosis pronounced with bright symptoms.
There are also chronic prostatitis in the exacerbation and chronic prostatitis phase in the remission phase.A cyclical course is characteristic of bacterial and non -infectious inflammation of the prostate gland.The exacerbation of chronic prostatitis leads to an increase in symptoms in both cases.
The Patanatomic (pathomorphological) classification of chronic prostatitis is of limited interest for patients and clinical doctors.
The causes of chronic prostatitis
Causes of chronic bacterial inflammation of the prostate gland
Chronic infectious prostatitis occurs due to tissue infection of the prostate gland.Most of the time, the cause of inflammation is E. coli or e.ColiLess commonly carved microbes of the genus Enterococcos, Klebsell, Proteus, Pseudomonas.
Like some other microbes, E. coli is able to form biofilms, thin, which consist of bacterial and firmly adjacent accumulations to the mucous membranes of the ducts.This explains why it is not always possible to cure chronic prostatitis.It is believed that the infection spreads as an ascending path through the urethra.However, the lymphogenic and hematogenous propagation of the infection is also possible.
The predisposing factors for the appearance of chronic infectious prostatitis are the following:
- sexually active age;
- Prostate adenoma or benign prostate hyperplasia;
- narrowing of the urethra;
- Unscrew the extreme meat of the penis;
- Bladder neck hypertrophy;
- Medical procedures (bladder catheterization, cystoscopy);
- Genetic and anatomical characteristics that predispose to the disease.
Causes of chronic non -bacterial inflammation of the prostate gland
The causes of chronic non -bacterial prostatitis are precisely unknown.Perhaps the disease is caused by viruses or bacteria, which are not identified during the bacterial secretion of the prostate gland.However, most scientists and doctors believe that prostatitis/CTB chronic (aseptic) is a poleetiological disease that occurs as a result of combinations of several adverse factors, namely:
- cycling;
- Irritation of the tissues of the prostate gland when the urine enters its ducts;
- Irritation of the prostate gland as a result of the use of any product or drink (especially with food allergies or celiacia);
- functional disorders of nervous innervation of the pelvic organs;
- Atrophy of the pelvic floor muscles;
- Stress, psycho -emotional loads;
- Pathology in the prostate gland, remaining after long -term acute prostatitis;
- hormonal disorders;
- Bladder diseases;
- Cold climate.
Since the exact causes of the disease are little known, the treatment of chronic prostatitis can be difficult.
Chronic prostatitis symptoms
Chronic (infectious) bacterial prostatitis is characterized by a cyclical course.The exacerbation phase is replaced by a remission phase.There are practically no symptoms between exacerbations.There is a clear connection among other diseases of the genitourinary organs: urethritis, epididimmets, cystitis.The cause of these pathologies, as a rule, is the same pathogen that causes chronic prostatitis.The symptoms during exacerbation are represented by dirty phenomena (frequent urine, rubber and ardor pain during urine) and pain with diverse intensity in the perineum, scrotum, sacrum, with irradiation in the penis.
The general condition is usually satisfactory.There are no signs of poisoning, there is no increase in body temperature.The prostate gland when examining the rectum (by straight) can be normal or slightly swollen, without acute pain characteristic of acute prostatitis.
Chronic non -bacterial (aseptic)/KTB prostatitis is characterized by pain in varying grades (from stupid to intense lungs) in the pelvis, perineum, sacrum and are the "visit card" of the disease (aseptic chronic prostatitis).The signs of inflammation of the prostate gland are expressed badly and are observed in 50% of cases.In other patients, they may be absent.
The presence of blood in sperm, painful ejaculation, defecation, dysosic phenomena are possible.The severity of the symptoms can change.The crotch is given pain, the rectum, which makes it difficult to find a person in sitting position.Fatigue, unreasonable fatigue, joint and muscular pains are also possible.Some patients complain about a decrease in sexual desire, erectile dysfunction (helplessness).
Asymptomatic chronic prostatitis has no characteristic symptoms of this disease, hence its name.During the laboratory study of the prostate secret, leukocytosis is determined, an increase in the levels of a specific prostate antigen is possible.There are no other signs of the disease.
Diagnosis of chronic prostatitis
The main methods to diagnose chronic infectious prostatitis are laboratory tests and topical tests that allow it to find out the source of leukocytes in urine and sperm.
A three -wall urine test helps identify inflammation.To do this, the patient urine three containers for analysis.The prostate massage between the second and third containers leads to stimulation of gland secretion.As a result, urine in the third container will contain the discharge of the prostate gland (leukocytes, red blood cells, bacteria), which is determined during the analysis.There is no need to massage the prostate especially and explore the pure secret of the gland.
The urine of the third container can be sent to a bacteriological examination with sowing to a nutrient medium.In the presence of bacterial growth, a test for the susceptibility of the pathogen to antibiotics is carried out.The method helps to perform treatment with greater precision and more effective.Since the prostate secret is a significant part of sperm, microscopy and ejaculated bacteria also allow the correct diagnosis.
Chronic (infectious) bacterial prostatitis is accompanied by a slight increase in PSA.Its level is reduced after successful treatment.Ultrasound and other instrumental studies do not have significant diagnosis value.
The diagnosis of prostatitis/CTB chronic non -bacterial (aseptic) can be difficult.Often, the diagnosis is made excluding other pathologies of the genitourinary tract and bacterial prostatitis.For this, instrumental and laboratory methods are used: urine microscopy (a three -wall test is also used after prostate massage), sperm or prostate secrets, followed by planting to a nutrient medium.The study list includes PSA analysis (differential diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory diseases of the prostate).
Microscopy reveals the presence of leukocytes in the urine, in the secret of the prostate, seed fluid with negative results of bacteriological treatment methods.Instrumental research methods (ultrasound, cystoscopy, MRI, CT) do not reveal signs of concomitant pathology.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
For successful treatment of chronic infectious prostatitis, rational and directed antibacterial therapy is necessary.Choice preparations are fluoroquinolones that create great concentrations of the drug in the tissues of the gland.The treatment course takes six to 12 weeks.Such duration of antibacterial therapy is necessary for a complete eradication of relapse infection and prevention.Second top drugs.
Bacterial chronic prostatitis can be cured with consistent and adequate therapy.Patients with frequent relapses should verify the immune state.It may also be necessary to exclude HIV infection, which is often the cause of the low effectiveness of antibacterial therapy.In such patients, it is possible to prescribe antibiotics at a sufficient dose to suppress bacterial growth.
The treatment of non -bacterial/KTS chronic prostatitis is difficult, since the infection is not the cause of chronic pain in the pelvis or passionate chronic prostatitis.It is necessary to seriously address the problem and answer the question of how to deal with a disease, whose cause is exactly unknown.
The absence of a certain etiology explains why the attempts to therapy of this pathology often do not succeed.
Chronic aseptic prostatitis treatment methods contain:
- Antibacterial therapy with fluoroquinolones (carried out by all patients).It is possible to have an infection that is not detected during a bacteriological examination.
- ALFA BLOCATORS.They contribute to the improvement of blood circulation in the prostate tissues.The effectiveness is low.
- NSAIDs and other anti -inflammatory medications have severe effectiveness, relieve pain and improve symptoms.However, the treatment is pathogenetic, after cancellation, the renewal of the disease is possible.
- Physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises (yoga, sport, active lifestyle), helping to improve blood circulation and eliminate venous stagnation, hypoxia, strengthening the pelvis muscles.The method helps patients with appropriate disorders.
- Antidepressants and anticonvulsive (effectiveness is not proven).
- Surgical treatment: laser or thin ablation of the prostate gland (not effective).
Forecast
In chronic infectious prostatitis in most patients, the prognosis is favorable.Consistent and adequate antibacterial therapy allows you to achieve success in more than 80% of cases.
Chronic non -bacterial (aseptic)/KTB prostatitis has the worst prognosis.The treatment helps only some patients.Others continue to suffer from chronic pain syndrome, despite the use of all available treatment methods.The disease has a pronounced effect on the psychomotional sphere and sexual relations.